Edit Photos Like a Pro Lightroom Photoshop 2025
Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do

For photographers and videographers, effective file storage is essential for managing large volumes of high-quality media. Proper storage ensures your data is secure, accessible, and organised, while providing the ability to back up files in case of failure. Below are common file storage options, along with best practices for each and the rationale behind them.
Best Practices:
Why:
Best Practices:
Why:
Best Practices:
Why:
Best Practices:
Why:
Best Practices:
Why:
Best Practices:
Why:
By choosing the right storage method for your needs, and following best practices, you can ensure your files remain safe, accessible, and organised.

No spam, notifications only about new blogs & updates.

Personal and business brand photographer and educator, super passionate about empowering business women and men to have a positive self perception, with the right tools and guidance so they can share their gifts with the world.

Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do

DSLR vs. Mirrorless in 2025: Which Should You Choose and Why It Matters In the fast-evolving world of photography, choosing
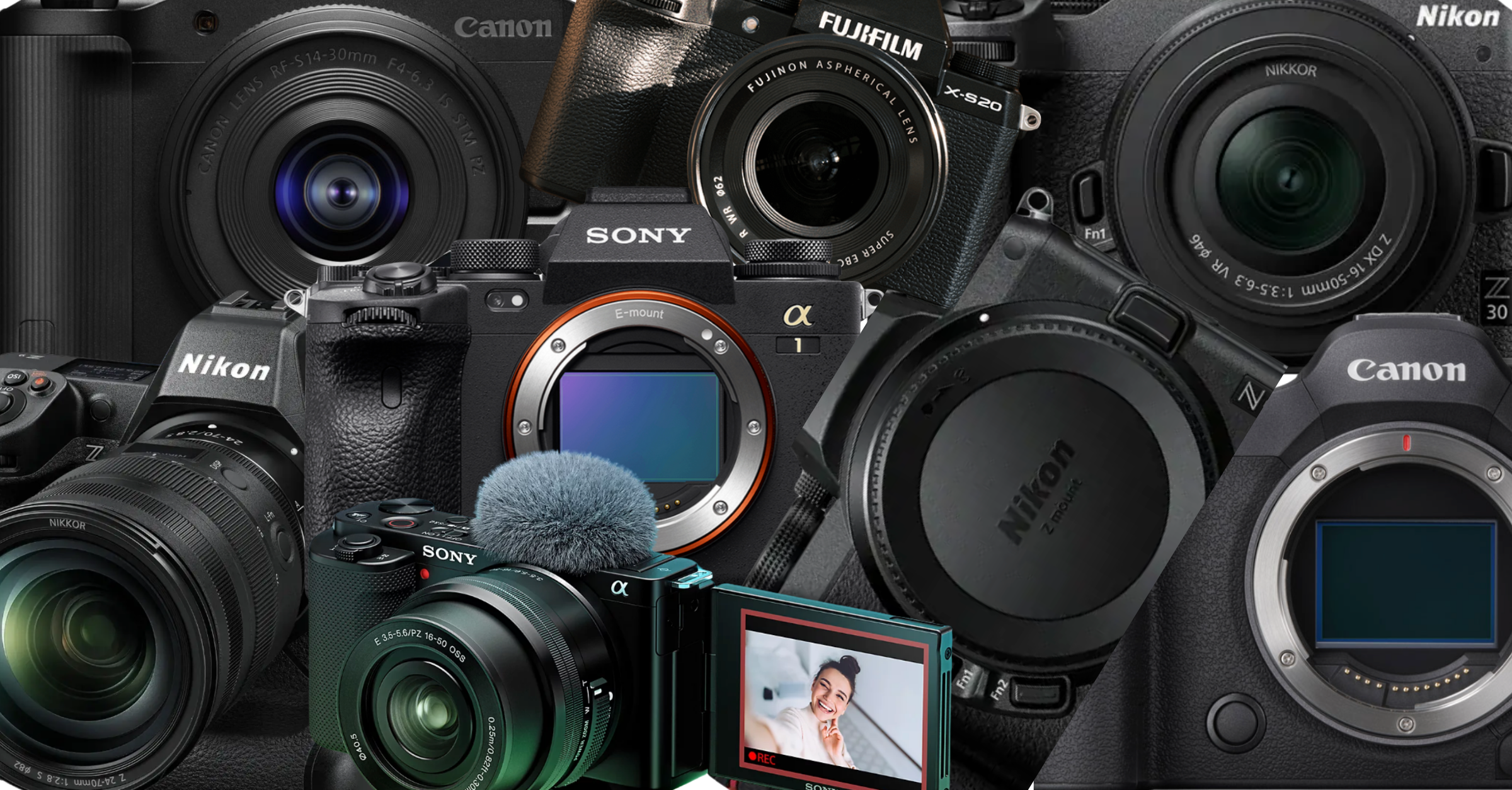

🔹 Best Cameras for Beginners (2025) 1. Canon EOS R50 Why: Compact, lightweight mirrorless with strong autofocus and image quality.

Mastering Low-Light Photography: Best Camera Settings With and Without Flash Low-light photography can be a creative playground or a technical

Why Posing Matters in Portrait Photography Posing isn’t about stiff limbs or forced smiles—it’s about bringing out the best in
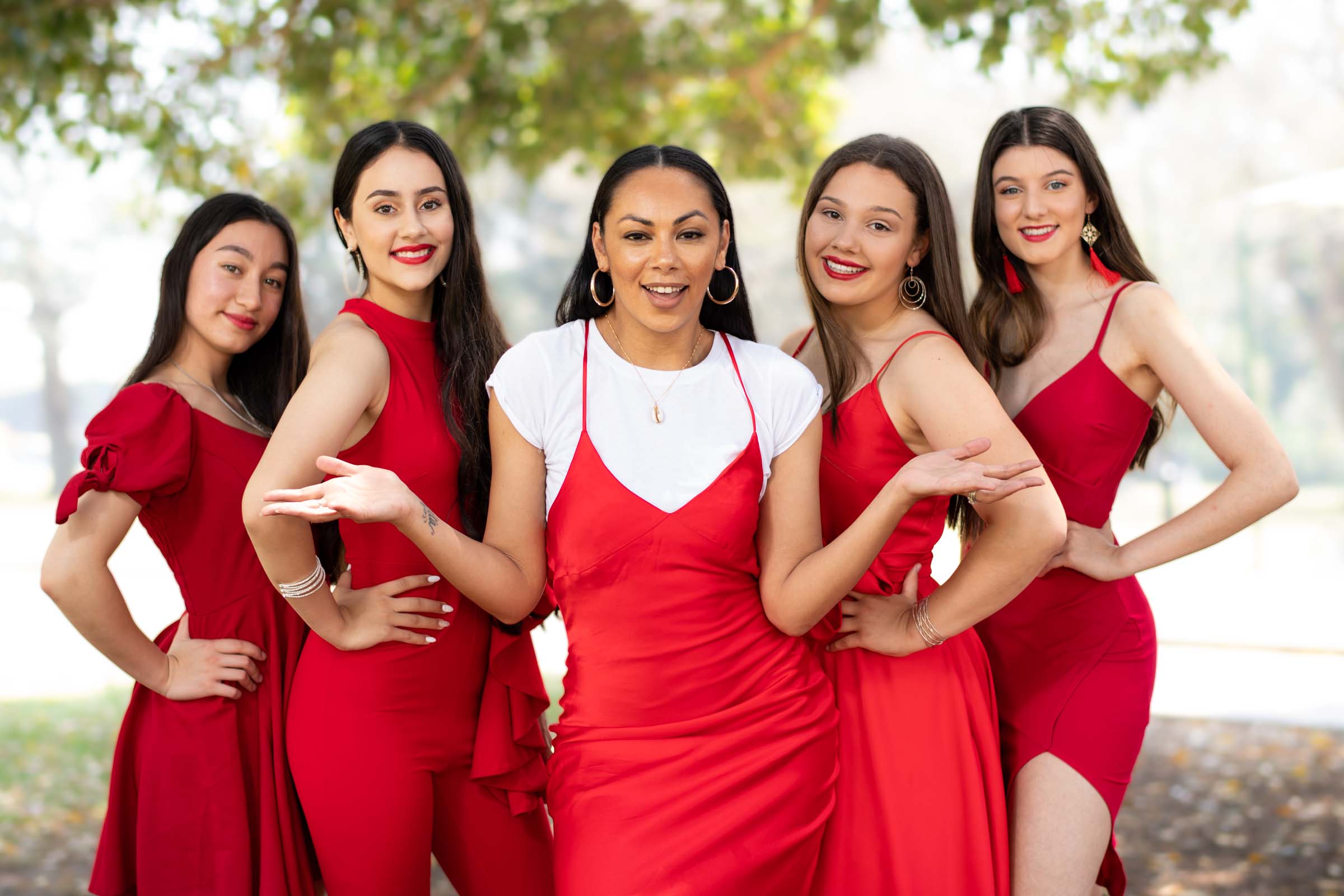

The Power of Open Body Language in Photography When it comes to capturing natural, powerful portraits, body language speaks louder
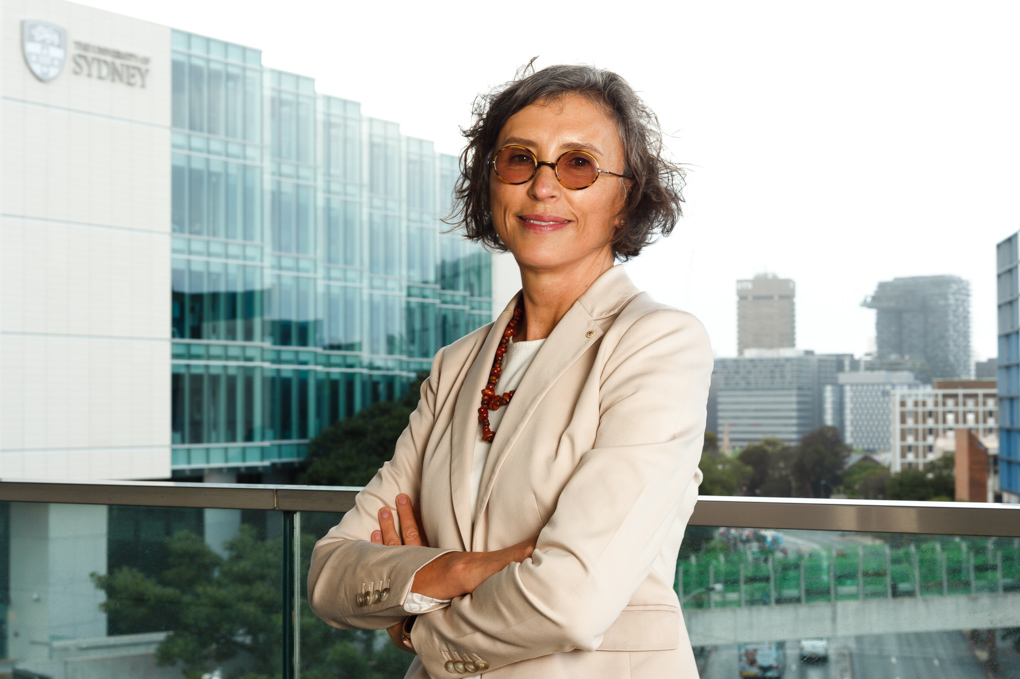

How Do I Balance Flash with Ambient Light Balancing flash with ambient light is a key skill that separates average

A Photographer’s Guide to Creative Expansion In photography, light isn’t just an element—it’s the language we speak.And when it comes
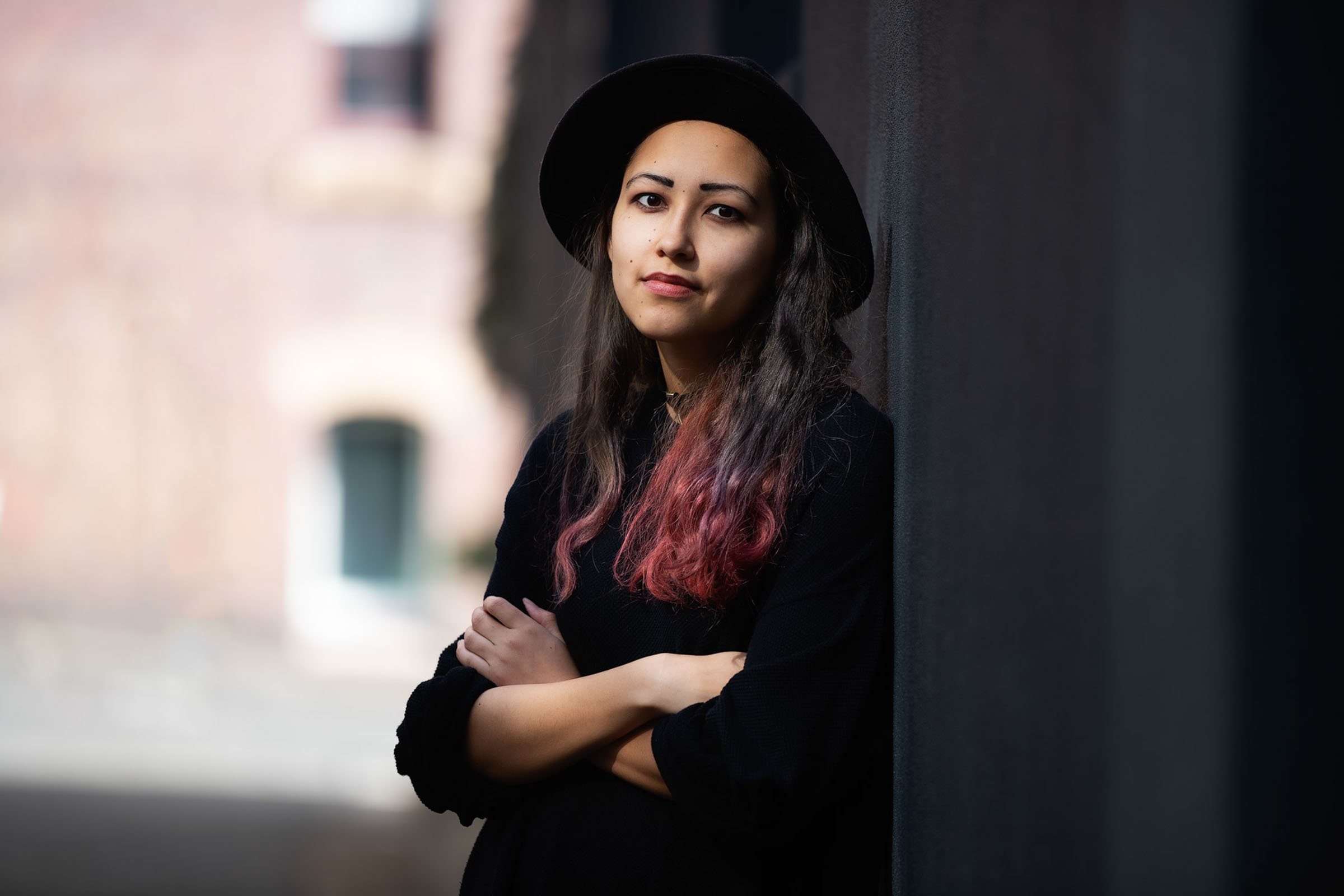

A Beginner’s Guide to Beautiful Lighting Natural light is one of the most beautiful and accessible tools in a portrait
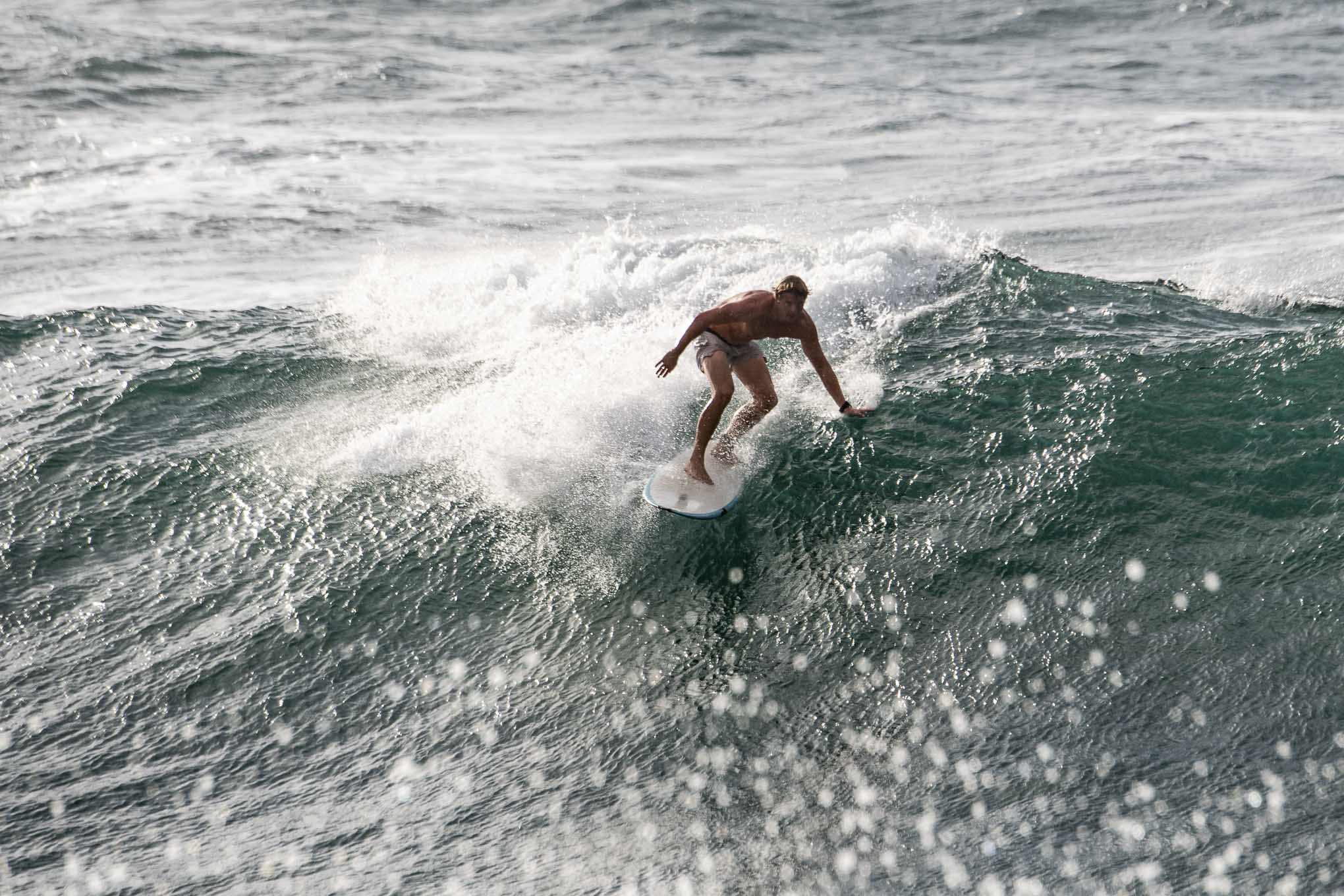

what you need to know Getting sharp images is a combination of good technique, the right settings, and proper camera

Many professional cameras offer dual card slots, allowing photographers and videographers to use two memory cards simultaneously. This feature enhances
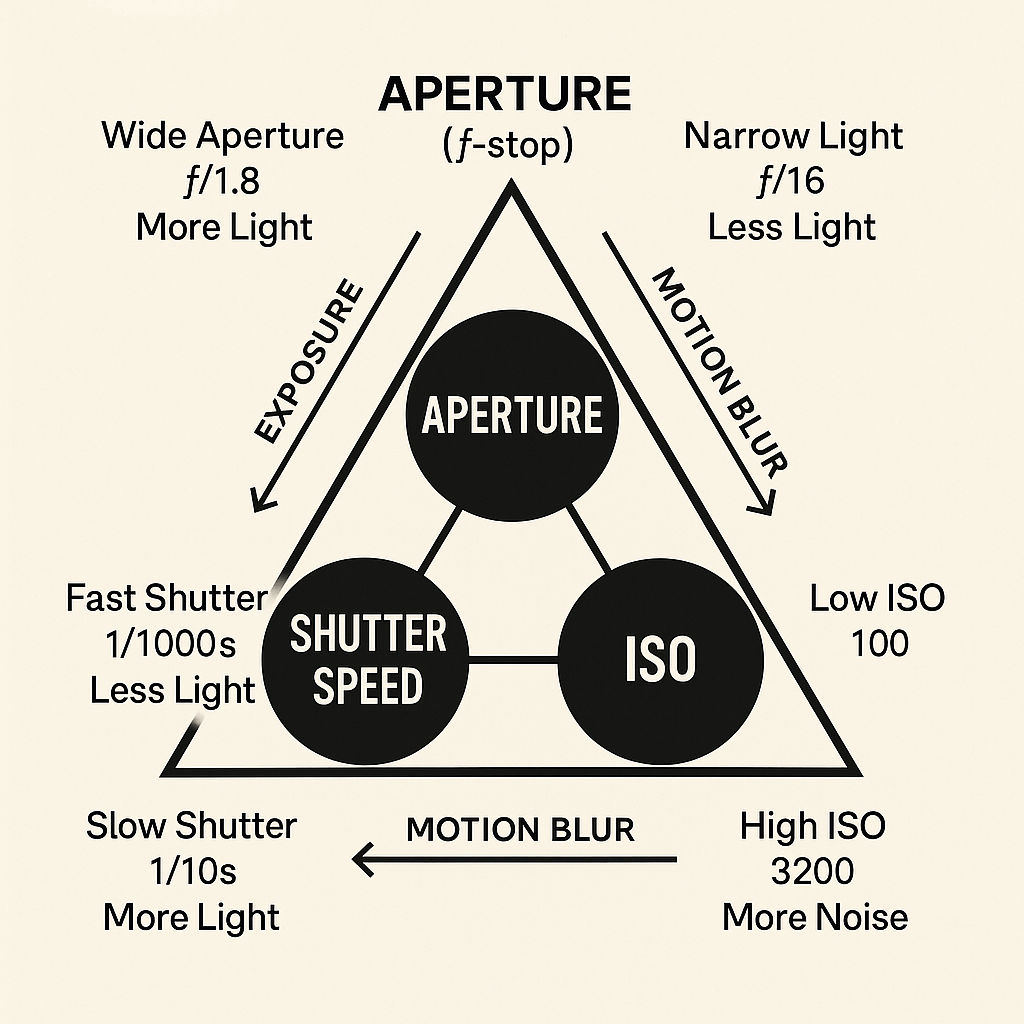
The exposure triangle The exposure triangle is a fundamental concept in photography that explains the relationship between three key elements