Edit Photos Like a Pro Lightroom Photoshop 2025
Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do you edit photos like a

When it comes to choosing a video format, understanding the differences between H.264, H.265, and RAW video is crucial for making the best decision based on the requirements of your project, storage limitations, and desired video quality. Below is a detailed comparison of these three formats, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and when each is best used.
Description: H.264 is one of the most widely used video compression formats. It provides a good balance of high-quality video at relatively low bitrates and is supported by almost every device and platform.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
When to Use:
Description: H.265 is the successor to H.264 and offers improved compression efficiency, allowing for higher video quality at a lower file size.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
When to Use:
Description: RAW video captures unprocessed footage directly from the camera’s sensor, preserving all the original data without any compression or processing. This allows for the highest quality and maximum flexibility in post-production.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
When to Use:
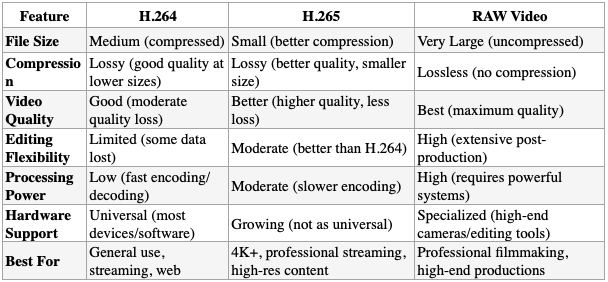
Choosing the right video format depends on your specific needs: H.264 for efficiency and broad compatibility, H.265 for cutting-edge compression and higher resolutions, and RAW video for the ultimate in image quality and post-production control.

No spam, notifications only about new blogs & updates.

Personal and business brand photographer and educator, super passionate about empowering business women and men to have a positive self perception, with the right tools and guidance so they can share their gifts with the world.


Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do you edit photos like a

DSLR vs. Mirrorless in 2025: Which Should You Choose and Why It Matters In the fast-evolving world of photography, choosing between a DSLR and a

🔹 Best Cameras for Beginners (2025) 1. Canon EOS R50 Why: Compact, lightweight mirrorless with strong autofocus and image quality. Sensor: APS-C Key Features: Dual

Mastering Low-Light Photography: Best Camera Settings With and Without Flash Low-light photography can be a creative playground or a technical challenge—often both. Whether you’re capturing

Why Posing Matters in Portrait Photography Posing isn’t about stiff limbs or forced smiles—it’s about bringing out the best in your subject. Whether you’re working

The Power of Open Body Language in Photography When it comes to capturing natural, powerful portraits, body language speaks louder than lighting, gear, or even

How Do I Balance Flash with Ambient Light Balancing flash with ambient light is a key skill that separates average photos from beautifully lit, professional-looking

A Photographer’s Guide to Creative Expansion In photography, light isn’t just an element—it’s the language we speak.And when it comes to natural light, we are

A Beginner’s Guide to Beautiful Lighting Natural light is one of the most beautiful and accessible tools in a portrait photographer’s toolkit. But to truly

what you need to know Getting sharp images is a combination of good technique, the right settings, and proper camera handling. Here’s what you need

Many professional cameras offer dual card slots, allowing photographers and videographers to use two memory cards simultaneously. This feature enhances workflow efficiency, data security, and
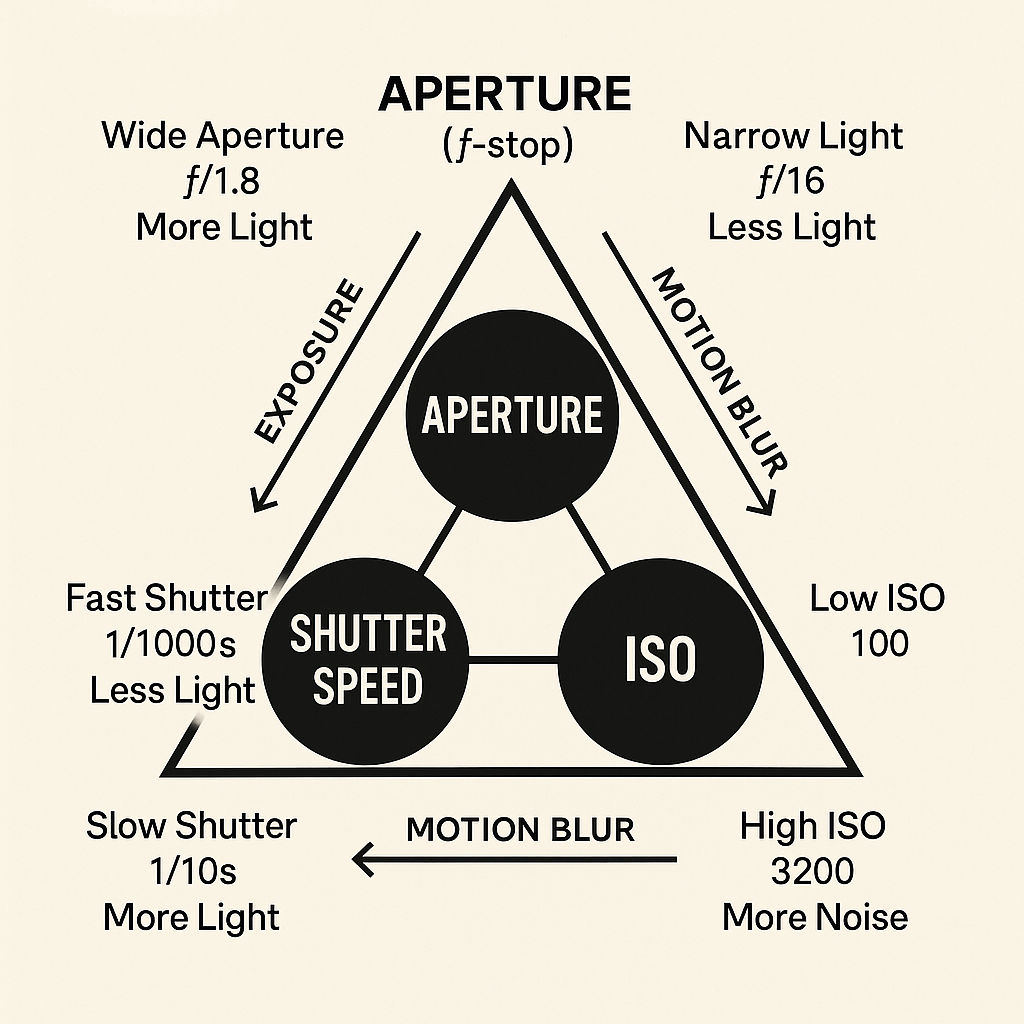
The exposure triangle The exposure triangle is a fundamental concept in photography that explains the relationship between three key elements that control the exposure (brightness