Edit Photos Like a Pro Lightroom Photoshop 2025
Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do

A Neutral Density (ND) filter is a photographic filter that reduces the intensity of light entering the lens without affecting the colour balance of the image. ND filters are essentially neutral grey filters, which allow photographers to use slower shutter speeds or wider apertures in bright conditions. This can result in creative effects or prevent overexposure in challenging lighting conditions.
ND filters reduce the amount of light passing through the lens by a specific number of stops, measured in f-stops. For example:
The filter darkens the image uniformly across the entire frame, hence the term “neutral”—it does not introduce any colour bias to the scene.
1. Long Exposure Photography in Daylight
One of the most popular uses of ND filters is for long exposure photography during daylight hours. When you use a slow shutter speed (e.g., 1/2 second or longer), the camera’s sensor collects light for an extended period. In bright daylight, this would result in overexposure. An ND filter allows you to reduce the amount of light hitting the sensor, enabling you to achieve the long exposure effect without overexposing the image. This is commonly used for:
2. Control Depth of Field in Bright Light
When shooting in bright light, it can be difficult to achieve a shallow depth of field (using a wide aperture like f/1.8 or f/2.8) without overexposing the image. An ND filter allows you to use a wider aperture by reducing the light entering the lens, enabling you to isolate subjects with a blurred background (bokeh effect), even in daylight.
3. Video Production
ND filters are also essential for filmmakers who want to shoot with a shutter speed of 1/50 or 1/60 (to create natural motion blur) but in bright daylight. By using an ND filter, filmmakers can reduce the light entering the lens, enabling them to achieve the desired shutter speed without overexposing the footage.
4. Balancing Exposure in High-Contrast Scenes
ND filters can be used creatively in high-contrast scenes, particularly when the sky is much brighter than the ground (e.g., landscapes or cityscapes). This helps maintain detail in both the highlights and shadows of the scene by allowing the photographer to adjust the exposure more evenly across the frame.
Neutral Density filters are invaluable tools for both photographers and videographers, offering creative control, preventing overexposure, and enabling unique long exposure effects even in bright conditions. The key to successfully using ND filters is selecting the right strength based on your needs and ensuring you’re using a high-quality filter that doesn’t degrade your image quality. Whether for landscape photography, video production, or portrait work, an ND filter is a versatile tool that can help you achieve stunning results in various lighting conditions.

No spam, notifications only about new blogs & updates.

Personal and business brand photographer and educator, super passionate about empowering business women and men to have a positive self perception, with the right tools and guidance so they can share their gifts with the world.

Mastering Creative Control📸 How to Edit Photos Like a Pro in Lightroom & Photoshop (2025 Creative Photographer’s Guide) How do

DSLR vs. Mirrorless in 2025: Which Should You Choose and Why It Matters In the fast-evolving world of photography, choosing

🔹 Best Cameras for Beginners (2025) 1. Canon EOS R50 Why: Compact, lightweight mirrorless with strong autofocus and image quality.

Mastering Low-Light Photography: Best Camera Settings With and Without Flash Low-light photography can be a creative playground or a technical

Why Posing Matters in Portrait Photography Posing isn’t about stiff limbs or forced smiles—it’s about bringing out the best in
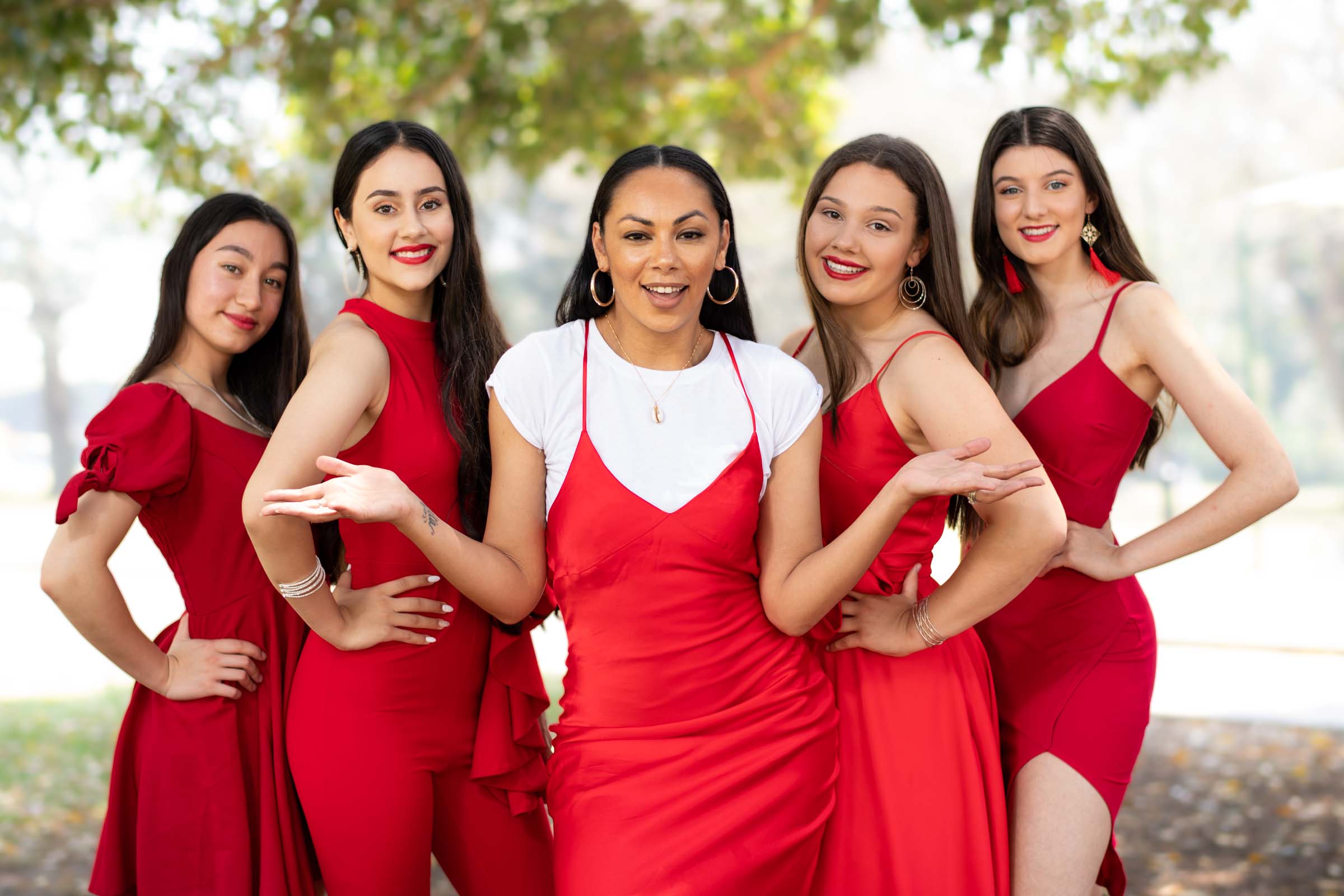

The Power of Open Body Language in Photography When it comes to capturing natural, powerful portraits, body language speaks louder
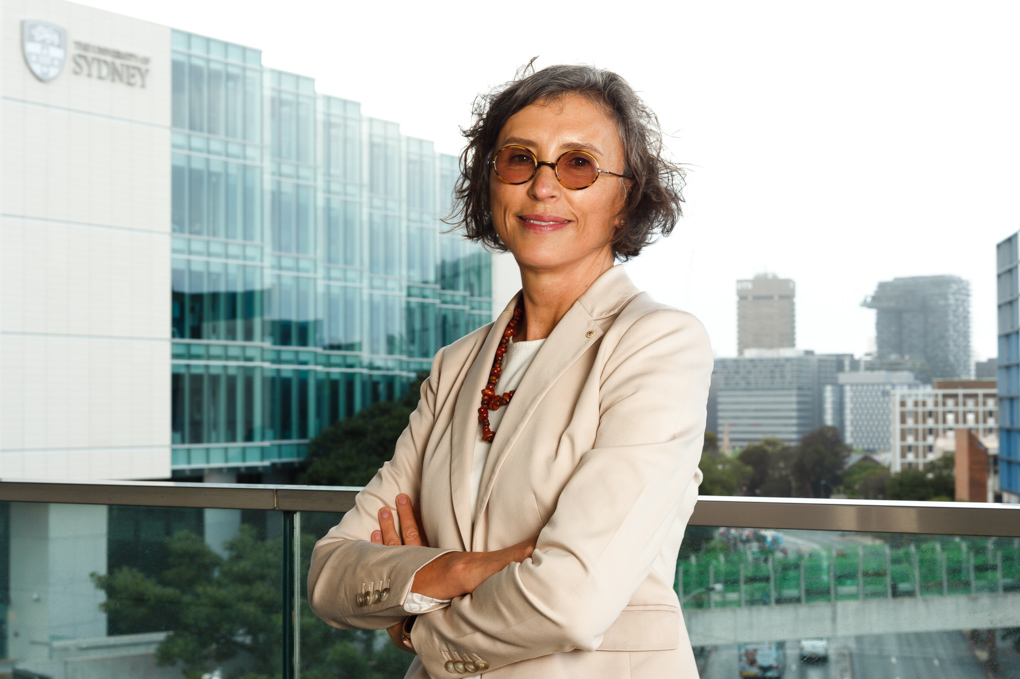

How Do I Balance Flash with Ambient Light Balancing flash with ambient light is a key skill that separates average

A Photographer’s Guide to Creative Expansion In photography, light isn’t just an element—it’s the language we speak.And when it comes
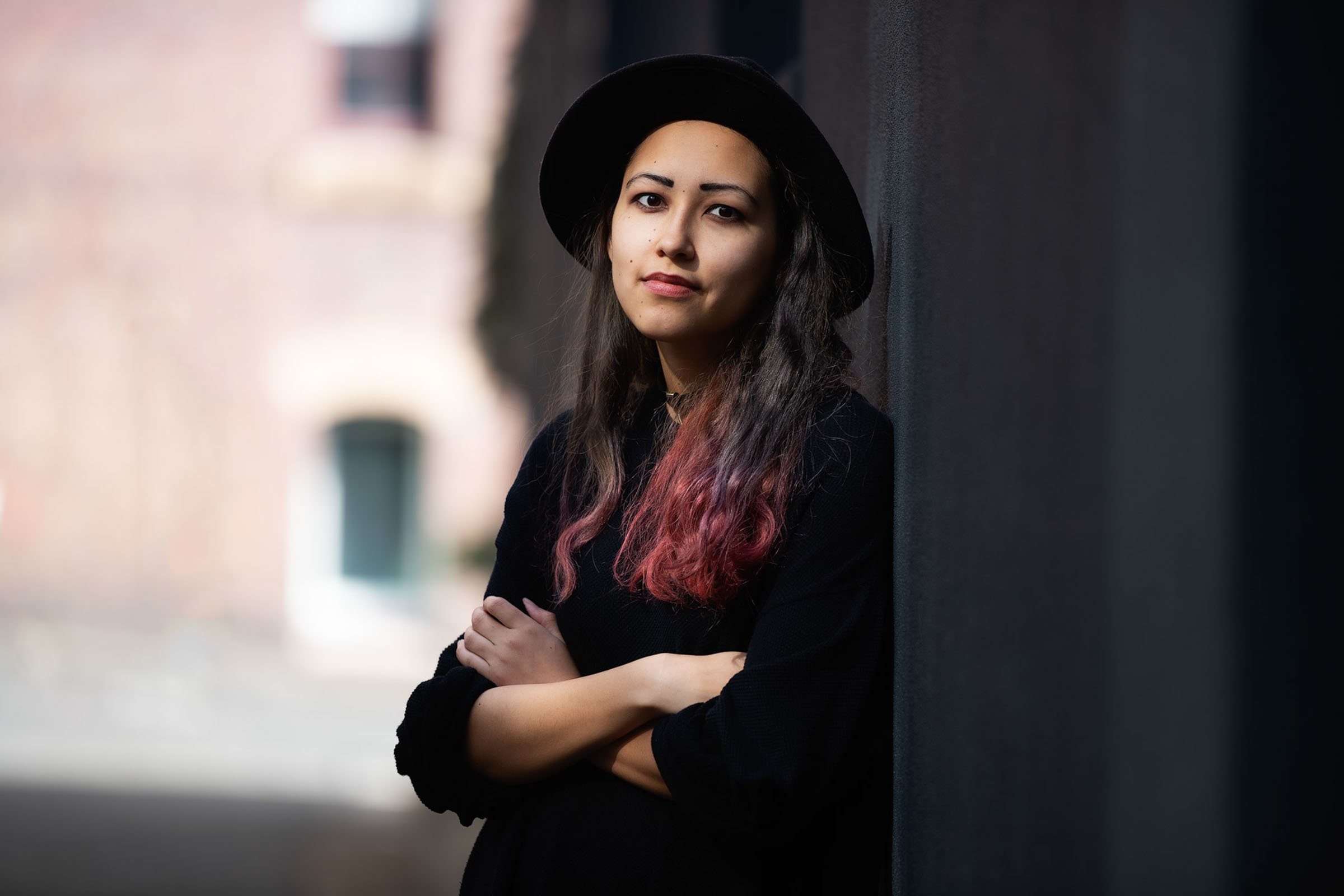

A Beginner’s Guide to Beautiful Lighting Natural light is one of the most beautiful and accessible tools in a portrait
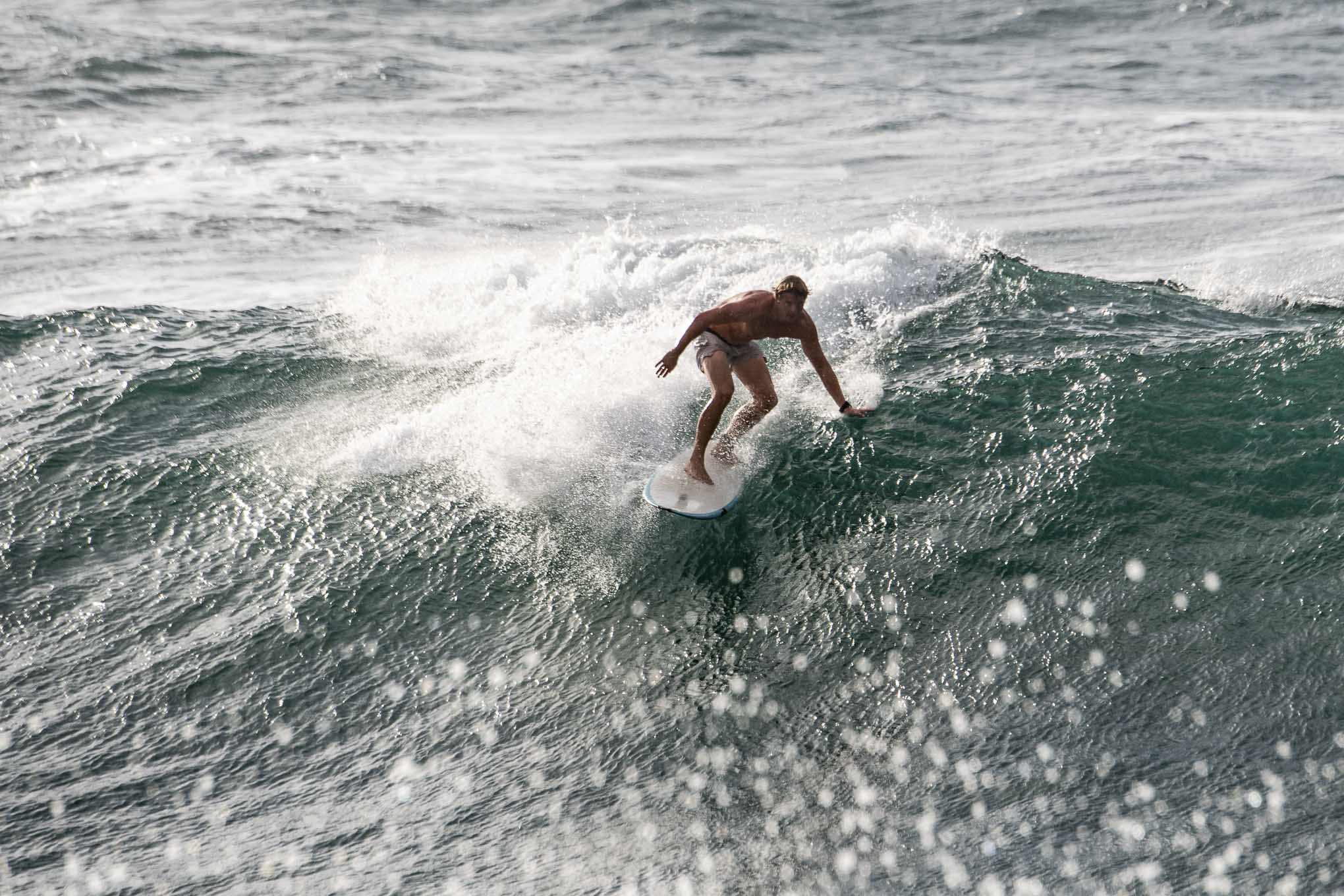

what you need to know Getting sharp images is a combination of good technique, the right settings, and proper camera

Many professional cameras offer dual card slots, allowing photographers and videographers to use two memory cards simultaneously. This feature enhances
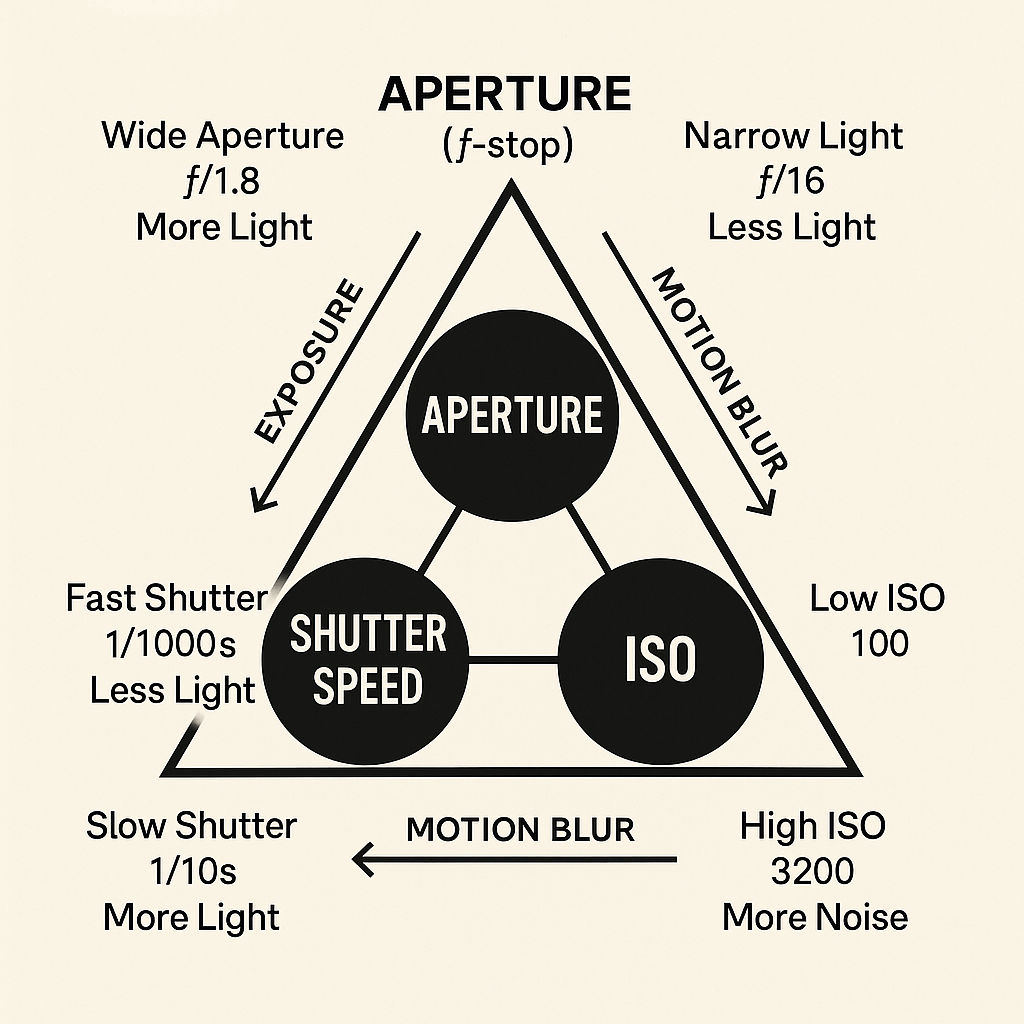
The exposure triangle The exposure triangle is a fundamental concept in photography that explains the relationship between three key elements